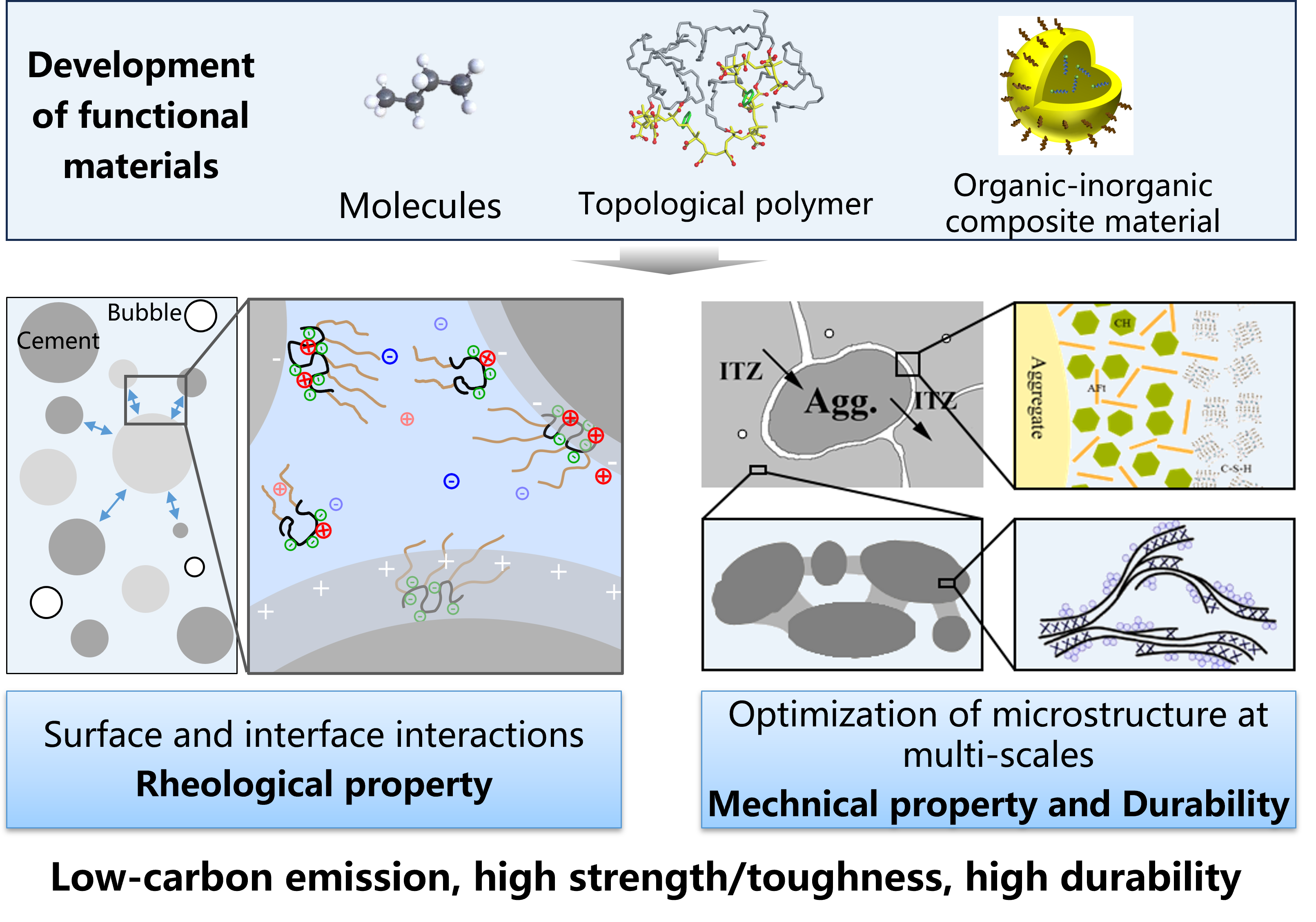
As China‘s engineering construction continues to advance towards complex and harsh environments, green, low-carbon, high toughness, and high durability have become the basic characteristics and requirements of modern concrete, while fluidity is the fundamental guarantee for the construction quality of concrete structures. This research direction focuses on the optimization and control of rheological and service performance of cement-based materials (including Portland cement, new low-carbon cementitious material systems, etc.). The main research objectives are as following: (a) the development and changes of cementitiousmaterial at nano-micro-macro scales during the hydration and hardening process; (b) development of functional materials (including small molecules, polymers, and organic-inorganic composite nano-micro materials); (c) optimization of rheological properties by the regulation of surface and interface interactions on/between solid particles and bubbles; (d)the enhancement of interaction between molecular chains, grains, and solid particles, and optimization of pore structure and defects, based on the regulation of the growth process of hydration products at different stages, to achieve high fluidity, high toughness, and high durability of concrete materials.
Selected publications:
(1) Han, K. D.; Guo, T. F.; Shu, X.*; Ran, Q. P.*. Understanding the thixotropic structural build-up of C3S pastes in the presence of polycarboxylate superplasticizers. Cem. Concr. Res., 2024, 184, 107625.
(2) Han, K. D.; Guo, T. F.; Shu, X.*; Ran, Q. P.*; Guo, Y. D.; Shi, J. Y. Insight into the role of early C3A hydration in structural build-up of cement paste. Cem. Concr. Res., 2024, 175, 107354.
(3) Meng, F.; Dong, L.*; Wu, Y. L.; Shu, X.*; Guo, Y. D.; Ran, Q. P.. Effects and mechanisms of capric acid/silica capsule on water absorption reduction of cement paste. Constr. Build. Mater., 2023, 404, 133208.
(4) Chen, J.; Shan, G. C.; Wu, J. Z.; Qiao, M.*; Gao, N. X.; Ran, Q. P.*. Branched alkyl polyethers as novel defoamers for concrete. Cem. Concr. Res., 2022, 157, 106821.
(5) Huang, Z.; Yang, Y.; Ran, Q. P.*; Liu, J. P. Preparing hyperbranched polycarboxylate superplasticizers possessing excellent viscosity-reducing performance through in situ redox initialized polymerization method. Cem. Concr. Compos., 2018, 93, 323-330.