二维过渡金属氧化物具有高理论容量、大比表面积和丰富的活性位点,因此被认为是极具潜力的储锂材料。但是,它们存在电导率低以及循环时体积变化大等缺点。此外,它们也难以在高负载(mass loading)状态下取得比商用石墨更高的面积比容量(~ 4 mA h cm−2)。
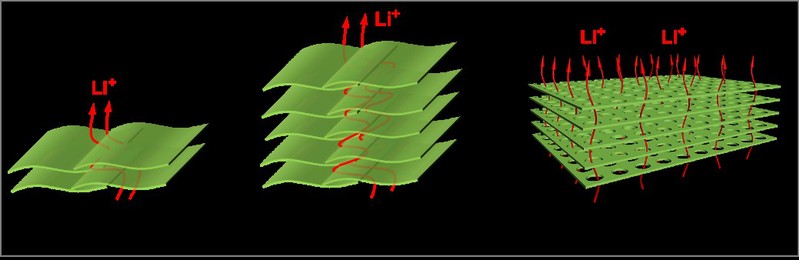
为此,本文提出了一种具有面内孔洞结构的多孔CoO(holey porous CoO, HPCO)纳米片。该HPCO纳米片是将我们前期制备的层状含钴水滑石(J. Mater. Chem. A, 2019, 7, 21264)进行退火而得到。随后HPCO纳米片表面被包覆一层10 nm左右的氮掺杂碳(nitrogen-doped carbon, NC),得到二维HPCO@NC纳米杂化材料。该纳米杂化材料在微观和宏观层面具有优异的协同效应:微观上,该纳米杂化材料有效地结合了HPCO和NC的组分与形貌优势,使其具有连续的锂离子和电子传输通道,并提供足够的结构柔韧性以缓解HPCO的体积变化;宏观上,面内孔洞结构可以为高负载量的电极提供互相连通的孔道,从而解决了高负载下锂离子扩散缓慢的动力学问题。基于这些优势,HPCO@NC纳米杂化材料在10 mg cm−2的高负载下可以获得高达7.1 mA h cm−2的面积比容量,这一数值是目前商业化石墨的1.8倍。因此,作者认为这样的holey porous结构也许能够推动二维金属氧化物在下一代高性能储锂材料中的应用。
该工作是与苏黎世联邦理工大学(ETH Zurich)Markus Niederberger教授合作完成。该工作得到了国家自然科学基金(51731004、51671054)、江苏省自然科学基金(BK20200386)、中央高校基本科研业务费专项资金、ETH Zurich的支持。该工作也得到了其他同事、老师和机构的大力帮助,在此一并感谢。
 |
文章信息:Long Pan,* Yicheng Wei, ZhengMing Sun*, Markus Niederberger, Layered hydrotalcites derived holey porous cobalt oxide nanosheets coated by nitrogen-doped carbon for high-mass-loading Li-ion storage, Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2020, 8, 26150–26157.
文章链接:https://pubs.rsc.org/en/content/articlehtml/2020/ta/d0ta08789k
Our group member Dr. Long Pan published together with Prof. Markus Niederberger their work on high-mass-loading Li+ storage of holey porous CoO nanosheets in Journal of Materials Chemistry A.
Brief Introduction: Nanosized 2D transition metal oxides (TMOs) are promising electrode materials for Li-ion batteries (LIBs) due to their theoretical high capacity, large specific surface area, and abundant active sites. However, they suffer from low conductivity and huge volume variation upon cycling. They also pose big experimental difficulties to realize areal capacities that are higher than that of commercial graphite (~4 mA h cm-2). Here we propose a novel strategy to prepare holey porous CoO (HPCO) nanosheets through annealing layered cobalt hydrotalcites followed by coating a thin layer (~10 nm) of nitrogen-doped carbon (NC). The resulting HPCO@NC nanohybrids deliver a good synergistic effect in addressing the abovementioned issues. Microscopically, the compositional and morphological integration of HPCO and NC equips the nanohybrids with continuous channels for both Li ions and electrons and with sufficient structural flexibility to accommodate the volume change. Macroscopically, the in-plane holey structure creates interconnected pathways in the thick electrode, thereby addressing the sluggish Li-ion diffusion kinetics at high mass loadings. As a result, the HPCO@NC nanohybrids deliver a high areal capacity of up to 7.1 mA h cm-2 at a high mass loading of 10 mg cm-2. This strategy may pave the way to realize the practical implementation of 2D TMOs towards next-generation LIB anode materials.
 |
Read it now: https://pubs.rsc.org/en/content/articlehtml/2020/ta/d0ta08789k
Long Pan, Yicheng Wei, ZhengMing Sun, Markus Niederberger, Layered hydrotalcites derived holey porous cobalt oxide nanosheets coated by nitrogen-doped carbon for high-mass-loading Li-ion storage, Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2020, 8, 26150–26157.